How Is The Us Divided Into Judicial Districts7 min read

How Is The Us Divided Into Judicial Districts?
The United States is divided into judicial districts, each with its own court system. There are 94 judicial districts in the United States. The judicial districts are organized into 13 circuits, each with a federal court of appeals. The districts are also organized into six regional circuits.
The first judicial district was created in 1789. The original district covered the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maryland, and Pennsylvania. In 1801, the district was divided into the Northern and Southern Districts. In 1807, the Eastern and Western Districts were created. In 1837, the Middle District was created.
The judicial districts are divided into two types: district courts and bankruptcy courts. District courts are the general trial courts of the federal judiciary. There are 91 district courts in the United States. Bankruptcy courts are courts of limited jurisdiction that hear bankruptcy cases. There are three bankruptcy courts in the United States.
The United States is divided into 13 circuits. The first circuit was created in 1801. The circuits are organized into six regional circuits. The regional circuits are the First Circuit, Second Circuit, Third Circuit, Fourth Circuit, Fifth Circuit, and Sixth Circuit.
The circuits are divided into two types: circuit courts and bankruptcy courts. Circuit courts are the intermediate appellate courts of the federal judiciary. There are 12 circuit courts in the United States. Bankruptcy courts are courts of limited jurisdiction that hear bankruptcy cases. There is only one bankruptcy court in the United States.
Table of Contents
How are the federal judicial districts divided up?
How are the federal judicial districts divided up?
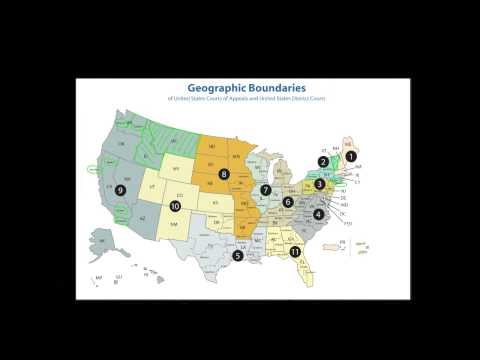
The federal judicial districts in the United States are divided up into two categories: the districts court and the circuit court. The districts court is the trial court, and the circuit court is the appellate court. There are 94 federal judicial districts in the United States, and each district is divided into one or more circuits.
The district court is a court of general jurisdiction. This means that the district court has the power to hear any case that is not specifically granted to another court. The district court is also the court of original jurisdiction for most lawsuits. This means that the district court is the court where a lawsuit is first filed.
The circuit court is an appellate court. This means that the circuit court hears appeals from the decisions of the district court. The circuit court is also the court of last resort for most lawsuits. This means that the circuit court is the court where a lawsuit is last filed.
There are six circuits in the United States. Each circuit is divided into several districts. The First Circuit is divided into the districts of Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. The Second Circuit is divided into the districts of Connecticut, New York, and Vermont. The Third Circuit is divided into the districts of Delaware, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. The Fourth Circuit is divided into the districts of Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia. The Fifth Circuit is divided into the districts of Louisiana and Texas. The Sixth Circuit is divided into the districts of Kentucky, Michigan, and Ohio.
How is the American judicial system structured?
The American judicial system is one of the most complex in the world. It is made up of three branches: the executive branch, the legislative branch, and the judicial branch. The executive branch is made up of the president and the cabinet. The legislative branch is made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate. The judicial branch is made up of the federal courts and the state courts.
The federal courts are the highest courts in the country. They are divided into two levels: the district courts and the appellate courts. The district courts are the trial courts. The appellate courts are the courts of appeal. They hear appeals from the district courts.
The state courts are the courts of first instance in the states. They are divided into two levels: the trial courts and the appellate courts. The trial courts are the courts where most criminal and civil cases are tried. The appellate courts are the courts of appeal. They hear appeals from the trial courts.
How many federal judicial districts are the 50 states divided into?

There are 94 federal judicial districts in the United States, including five territories. The 50 states are divided into 94 judicial districts, including five territories.
How is the judicial branch distributed?
The judicial branch is one of the three branches of the United States government. It is made up of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts. The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws passed by Congress and the Constitution.
The Supreme Court is made up of nine justices. These justices are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country and can hear cases from any of the lower federal courts.
The lower federal courts are made up of the district courts, the courts of appeals, and the bankruptcy courts. These courts are responsible for hearing cases that arise under federal law. The district courts are the trial courts, and the courts of appeals are the appellate courts. The bankruptcy courts are special courts that hear cases involving bankruptcy.
What is the major division of the U.S. court system?
The United States court system is divided into three major branches: the federal court system, the state court system, and the local court system.
The federal court system is the national court system. It administers justice in the United States and is made up of the U.S. Supreme Court, the U.S. Courts of Appeals, and the U.S. District Courts.

The state court system is the court system of each of the 50 U.S. states. It is made up of the state supreme court, the state courts of appeal, and the state trial courts.
The local court system is the court system of each of the more than 3,000 counties and municipalities in the United States. It is made up of the inferior trial courts, the superior trial courts, and the appellate courts.
How many U.S. districts are there?
In the United States, there are 435 congressional districts. These districts are represented in the House of Representatives by a member of Congress. The number of districts is based on the population of the state. The more people in a state, the more districts that state has in the House of Representatives.
What are the three levels of judiciary?
In most democracies, the judiciary is divided into three levels: the lower courts, the appellate courts, and the supreme court.
Lower courts are the first stop for most legal disputes. They include trial courts and smaller courts that deal with specific kinds of cases, like traffic court or small-claims court. Appellate courts hear appeals from decisions made by lower courts. They may also hear cases that were originally heard by a lower court, but were later appealed. The supreme court is the highest court in the country, and is responsible for deciding disputes about the interpretation of the law and the constitution.
The structure of the judiciary varies from country to country. In some countries, the supreme court is the only level of appellate court. In others, there are several levels of appellate court. And in still others, there are several levels of trial court as well.
The role of the judiciary is to interpret and apply the law. This can be a complicated task, as the law can be interpreted in different ways, and it can be difficult to apply the law to specific situations. The judiciary is also responsible for ensuring that the government acts within the law, and that the rights of individuals are protected.
The independence of the judiciary is a key principle of democracy. This means that the judiciary is separate from the other branches of government, and that it is not subject to political interference. This ensures that the judiciary can act independently, and make decisions based on the law, not on politics.
