Legal Entity For Business12 min read
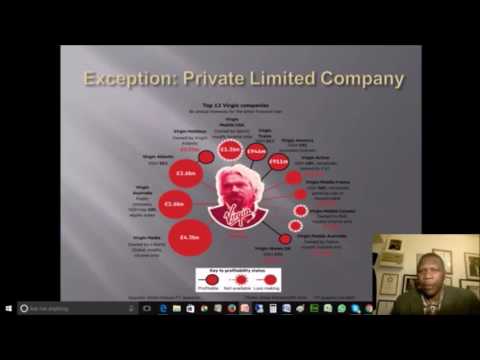
There are many legal entities a business can choose from when starting out, but what are they and what are the benefits of each?
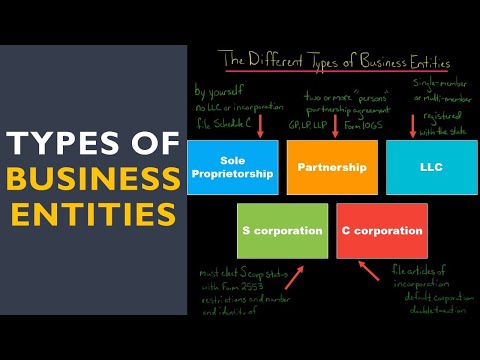
The most common legal entities are sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), and corporations. The best entity for your business depends on your individual situation, but each type of entity has its own benefits and drawbacks.
Sole proprietorships are the simplest form of business entity. The business and the owner are one and the same, so the business is not legally separate from the owner. This can be a drawback because the owner is personally liable for all the business’s debts and liabilities. On the other hand, sole proprietorships are easy and inexpensive to set up, and they offer the greatest tax flexibility.
Partnerships are similar to sole proprietorships, but they involve two or more owners. Like sole proprietorships, partnerships are not legally separate from their owners and have no separate legal identity. This can be a drawback because the partners are personally liable for the business’s debts and liabilities. On the other hand, partnerships offer the partners more flexibility and tax advantages than sole proprietorships.
Limited liability companies (LLCs) are a newer type of business entity that offers the benefits of both partnerships and corporations. LLCs are separate legal entities, so the owners are not personally liable for the company’s debts and liabilities. LLCs offer the owners more flexibility and tax advantages than corporations, but more protection from personal liability than partnerships.
Corporations are the most complex type of business entity, but they offer the greatest protection from personal liability. Corporations are separate legal entities, so the owners are not personally liable for the company’s debts and liabilities. Corporations also offer the owners more flexibility and tax advantages than LLCs.
When choosing a business entity, it’s important to consider the benefits and drawbacks of each type and to choose the one that’s best for your individual situation.
Table of Contents
What are the 5 main types of legal entity a business can be?
There are many different types of legal entities a business can be. The most common are sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, limited liability company (LLC), and S corporation. Each type of entity has different benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the right one for your business.
Sole proprietorship is the simplest type of business entity. It’s just you and your business, and you’re responsible for everything. This can be a good option for small businesses, because there are no legal or administrative costs to set it up. However, you’re also responsible for any debts or liabilities your business accrues.
A partnership is similar to a sole proprietorship, but it involves two or more people. Like a sole proprietorship, there are no legal or administrative costs to set it up, and you’re responsible for any debts or liabilities your business accrues. However, partnerships can be more complicated than sole proprietorships, and you need to make sure you have a written partnership agreement in place.
A corporation is a more formal business entity. It has its own legal existence, and is separate from its owners. This can be a good option for larger businesses, because it offers more liability protection for the owners. However, corporations can be more expensive and complicated to set up and maintain.
A limited liability company (LLC) is a newer business entity that combines the benefits of a corporation and a partnership. It offers limited liability protection for its owners, and is less expensive and complicated to set up than a corporation. However, LLCs are not as well-known as other business entities, so it may be more difficult to find investors or lenders.
An S corporation is a special type of corporation that offers some of the benefits of a partnership. Like an LLC, it offers limited liability protection for its owners, and is less expensive and complicated to set up than a regular corporation. However, S corporations are subject to special rules and restrictions, so you need to make sure you meet all the requirements.
What are the 4 business entity types?
There are four types of business entities: Corporations, Limited Liability Companies (LLC’s), Sole Proprietorships, and Partnerships. Each one has its own set of rules and regulations, and choosing the right one for your business is important.
A Corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners, and is the most common type of business entity. Owners are called shareholders, and they have limited liability for the company’s debts and obligations. This means that if the company goes bankrupt or is sued, the shareholders are not liable for any of the company’s losses. A Corporation must have a Board of Directors, and is subject to a variety of rules and regulations from the government.

A Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a newer type of business entity, and is a cross between a Corporation and a Partnership. LLC’s offer the limited liability of a Corporation, but are less regulated and are often simpler to set up than a Corporation. Owners of an LLC are called members, and they are not personally liable for the company’s debts or obligations.
A Sole Proprietorship is the simplest type of business entity, and is owned by one person. The owner is personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations, and there is no separation between the company and the owner. Sole Proprietorships are easy to set up and are the most common type of business in the United States.
A Partnership is owned by two or more people, and is the most common type of business entity in the United States. Partners are personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations, and there is no separation between the company and the partners. Partnerships are easy to set up, and can be a great option for small businesses.
What are the 5 entity types?
There are 5 entity types in the world: natural, legal, business, nonprofit, and government. Each type has its own unique characteristics and purpose.
Natural entities are entities that exist naturally, such as plants and animals. They are not created by humans and have no legal status.
Legal entities are entities that are created by humans and have a legal status. The most common type of legal entity is a corporation, which is a company that is separate from its owners. Other types of legal entities include partnerships and limited liability companies.
Business entities are entities that are created for the purpose of conducting business. The most common type of business entity is a corporation, which is a company that is separate from its owners. Other types of business entities include partnerships and limited liability companies.
Nonprofit entities are entities that are created for the purpose of serving a public purpose, such as a charity or a school. Nonprofit entities are not allowed to distribute profits to their owners.
Government entities are entities that are created by the government to serve a public purpose. The most common type of government entity is a municipality, which is a city or town. Other types of government entities include states and countries.
What do I put for legal entity?
When starting a business, you will need to decide what legal entity to form. This will determine the structure and regulations of your business. There are several types of legal entities, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common legal entities are:
– Sole proprietorship
– Partnership
– Limited liability company (LLC)
– Corporation
Sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common type of business. There is no legal distinction between the business and the owner, so the owner is personally liable for all business debts and obligations.

Partnership is similar to a sole proprietorship, but involves two or more owners. Like a sole proprietorship, the partners are personally liable for all business debts and obligations.
Limited liability company (LLC) is a newer type of business entity that offers some of the benefits of a corporation, without the added complexity and cost. An LLC offers limited liability for its owners, meaning that they are only liable for the amount of money they have invested in the company. The company is also treated as a separate legal entity, which can provide some protection against personal liability.
Corporation is the most complex and expensive type of business entity. A corporation is a separate legal entity, with its own tax ID number and legal status. This provides the greatest level of protection from personal liability. The corporation is also subject to its own set of rules and regulations.
What is an example of a legal entity?
A legal entity is an organization or individual that has been granted limited liability protection by the government. Legal entities are typically formed by filing Articles of Organization with the state in which they will operate.
There are a variety of different types of legal entities, but the most common are corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs). Corporations are owned by shareholders, who have limited liability for the debts and obligations of the company. LLCs are owned by members, who also have limited liability for the company’s debts and obligations.
Other common legal entities include partnerships, sole proprietorships, and nonprofits. Partnerships are owned by partners, who are jointly and severally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. Sole proprietorships are owned by a single individual, who is liable for the company’s debts and obligations. Nonprofits are organizations that are not for profit and are typically exempt from income taxes.
Legal entities offer a number of advantages over sole proprietorships and partnerships. The most significant advantage is limited liability protection. This means that the owners of the company are not personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. This can be especially important in the event that the company is sued or goes bankrupt.
Legal entities also offer a number of administrative advantages. Corporations and LLCs have a number of formalities that must be followed in order to maintain their limited liability protection. This includes things like maintaining corporate minutes and filing annual reports. This can be a burden for sole proprietors and partnerships, which typically do not have these formalities.
Legal entities also offer a number of tax advantages. For example, corporations and LLCs are able to take advantage of tax deductions that sole proprietorships and partnerships are not. This can result in a lower tax bill for the company.
Overall, legal entities offer a number of advantages over sole proprietorships and partnerships. The most significant advantage is limited liability protection, which can protect the owners of the company in the event that the company is sued or goes bankrupt. Legal entities also offer a number of administrative and tax advantages.
How do I choose an entity type?
When starting a business, one of the first decisions you have to make is what type of legal entity to establish. This decision will have a major impact on how your business is structured and taxed.
There are several factors to consider when choosing an entity type:
1. Limited Liability
One of the primary benefits of incorporating or forming an LLC is limited liability. This means that the owners of the company are protected from personal liability for the company’s debts and liabilities. If the company goes bankrupt or is sued, the owners’ personal assets are generally safe.
2. Taxation
Another important factor to consider is how the entity will be taxed. The two main types of taxation are pass-through taxation and entity taxation.
Pass-through taxation means that the company’s income is taxed at the individual level. This is the default taxation method for LLCs and sole proprietorships.
Entity taxation means that the company is taxed as a separate entity. This is the default taxation method for corporations.
3. Ownership
Another important factor to consider is the type of ownership structure. The most common ownership structures are sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, and corporation.
Sole proprietorship is owned by one individual and is the simplest type of business structure. Partnership is owned by two or more individuals and is also fairly simple. LLCs are owned by one or more individuals and offer limited liability protection. Corporations are owned by one or more individuals and offer the most complex ownership structure.
4. Regulations
Finally, you should consider the regulations that apply to the entity type you choose. For example, certain entity types are subject to specific regulations and requirements, such as LLCs and corporations.
What legal entity means?
When starting a business, one of the first decisions to make is what legal entity to form. This is a complex decision, and there are a number of factors to consider.
The first step is to understand the different types of legal entities. The most common types are corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and partnerships.
A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners. This means that the corporation can own property, enter into contracts, and sue and be sued. The owners of a corporation are called shareholders.
An LLC is a separate legal entity from its owners, but its owners are protected from personal liability. This means that the LLC’s owners cannot be sued for the LLC’s debts or obligations.
A partnership is not a separate legal entity. This means that the partnership’s owners are personally liable for the partnership’s debts and obligations.
The next step is to decide which type of legal entity is best for your business. There are a number of factors to consider, including taxation, ownership, and liability.
The most important factor to consider is taxation. Corporations and LLCs are taxed separately from their owners, while partnerships are not. This means that the business income and losses are taxed at the individual owner level.
The next factor to consider is ownership. Corporations and LLCs have shareholders or members, while partnerships have partners.
The final factor to consider is liability. Corporations and LLCs offer limited liability to their owners, while partnerships do not. This means that the owners of a corporation or LLC are protected from personal liability for the corporation’s or LLC’s debts and obligations.
There are a number of other factors to consider when deciding which legal entity to form, including formation costs, ongoing compliance costs, and the availability of state and federal benefits.
It is important to consult with an attorney when making this decision. An attorney can help you understand the different types of legal entities and determine which is best for your business.
