Poder Judicial De Chile8 min read

The Chilean judiciary is one of the three branches of government in Chile, along with the executive and the legislative. It is independent of the executive and the legislative branches, and is responsible for the interpretation and application of the law. The judiciary is made up of the Supreme Court, the lower courts, and the tribunals.
The Supreme Court is the highest court in Chile. It is made up of fifteen judges, who are appointed by the president with the consent of the Senate. The Supreme Court is responsible for the interpretation and application of the law, and for the administration of justice.
The lower courts are the courts of first instance, and are divided into civil, criminal, labor, and family courts. The lower courts are responsible for the administration of justice in their respective areas of jurisdiction.
The tribunals are specialised courts that deal with specific areas of law, such as the tax court, the environmental court, and the military court. The tribunals are responsible for the interpretation and application of the law in their respective areas of jurisdiction.
The Chilean judiciary is a separate and independent branch of government, and is responsible for the interpretation and application of the law. The Supreme Court is the highest court in Chile, and is responsible for the administration of justice. The lower courts are the courts of first instance, and are responsible for the administration of justice in their respective areas of jurisdiction. The tribunals are specialised courts that deal with specific areas of law, and are responsible for the interpretation and application of the law in their respective areas of jurisdiction.
Table of Contents
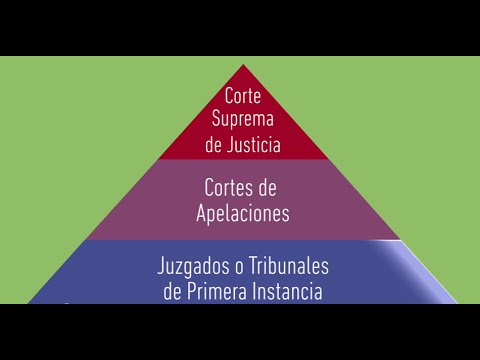
¿Qué es el Poder Judicial en Chile?
The Judiciary is one of the three powers of the state, together with the Executive and the Legislative. It is responsible for the impartial application of the law.
The Judiciary in Chile is composed of the Supreme Court, the Courts of Appeal, the Courts of First Instance and the Military Courts.
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country and is responsible for interpreting and applying the law. It has final say on all legal matters.
The Courts of Appeal are responsible for hearing appeals from decisions of the Courts of First Instance.
The Courts of First Instance are the main trial courts in the country and are responsible for hearing most criminal and civil cases.
The Military Courts are responsible for hearing cases involving members of the military.
¿Dónde puedo ver mis causas judiciales?

If you’ve ever been involved in a legal dispute, you may be curious about the progress of your case. Fortunately, there are a few ways to track your case online.
The first option is to check the website of the court where your case is being heard. Most court websites have a section where you can view the status of your case. This section will usually list the case number, the name of the plaintiff and defendant, and the current status of the case.
Another option is to use the online portal of the Ministry of Justice. This portal allows you to search for information on all court cases in Argentina. You can view the status of each case, as well as the court where the case is being heard and the date of the next hearing.
Finally, you can use the website of the National Registry of Judicial decisions. This website allows you to search for court decisions by name, case number, or type of decision. You can also view the status of each case and the court where it is being heard.
¿Cómo saber si tengo causas judiciales en Chile?
Chile is a country in which anyone can access information about judicial proceedings that are taking place against them. This is done through the Registro de causas judiciales, which is a public registry that is kept by the Ministry of Justice.
In order to access this registry, you can go to the website of the Ministry of Justice, or you can go to the Registro Civil (Civil Registry) and request information about any judicial proceedings that are taking place against you.
Keep in mind that there is a fee for obtaining this information, and the amount of the fee will depend on the type of information that you are requesting.
If you want to obtain information about proceedings that are taking place in another municipality, you will need to go to the Registro de causas judiciales de ese municipio (Registry of Judicial Proceedings in that Municipality).
The Registro de causas judiciales is a very useful resource for anyone who wants to know whether or not they have any judicial proceedings taking place against them.
¿Cómo es el examen de ingreso al Poder Judicial 2021?
El examen de ingreso al Poder Judicial 2021 se realizará el 9 de agosto. Será una prueba objetiva de 100 preguntas.
Las materias que se evaluarán son Derecho Constitucional, Derecho Civil, Derecho Penal, Derecho Laboral y Derecho Administrativo.

Los aspirantes deberán contestar un mínimo de 60 preguntas para poder rendir el examen.
Las preguntas serán de tipo test, con cuatro opciones de respuesta, solamente una de las cuales es correcta.
Los aspirantes podrán consultar las respuestas una vez finalizado el examen.
El examen se podrá realizar en forma presencial o por Internet.
Para presentarse al examen de ingreso al Poder Judicial 2021 es requisito estar inscripto en el Registro Nacional de Abogados.
El costo de la inscripción es de $ 1.500.
El plazo de inscripción finaliza el 7 de agosto.
¿Qué es el Poder Judicial y cuáles son sus funciones?
El Poder Judicial es una institución integrada por órganos que ejercen el poder de juzgar y hacer cumplir la ley. Sus funciones son: administrar justicia, interpretar y aplicar la ley, velar por el respeto de los derechos humanos y hacer efectiva la tutela judicial.
En Argentina, el Poder Judicial está conformado por la Corte Suprema, las Cámaras de Apelaciones, los Tribunales Orales en lo Criminal y en lo Civil y los Juzgados de Primera Instancia.
El objetivo de la Corte Suprema es preservar el orden constitucional y garantizar la independencia de los poderes del Estado. Las Cámaras de Apelaciones tienen como función revisar los fallos de primera instancia, mientras que los Tribunales Orales en lo Criminal y en lo Civil juzgan los delitos y las acciones civiles. Por último, los Juzgados de Primera Instancia tienen a su cargo la resolución de asuntos de menor cuantía.
¿Cuál es el rol del Poder Judicial?
El Poder Judicial tiene como principal función la administración de justicia, es decir, velar por que las leyes se cumplan y juzgar a las personas que las incumplan. Además, el Poder Judicial es el encargado de garantizar los derechos fundamentales de las personas.
Para cumplir con estas funciones, el Poder Judicial tiene atribuciones como:
– Interpretar y aplicar las leyes
– Resolver conflictos entre personas o entre personas y el Estado
– Garantizar los derechos fundamentales de las personas
El Poder Judicial es independiente del Ejecutivo y del Legislativo, es decir, no está subordinado a ninguno de ellos.
¿Cómo buscar una causa judicial con el RUT?
Cuando se tiene un problema legal, una de las primeras cosas que se debe hacer es buscar la causa judicial correspondiente. Sin embargo, encontrar el juicio adecuado puede ser una tarea complicada si no se cuenta con el RUT de la persona o del negocio involucrado.
El RUT (Registro Único de Tributación) es un código de identificación fiscal que permite buscar información sobre personas y empresas en el Servicio de Impuestos Internos (SII). Por lo tanto, si se tiene el RUT de la persona o empresa en cuestión, es mucho más fácil encontrar el juicio correspondiente.
En primer lugar, se debe ingresar el RUT en el buscador del SII (www.sii.cl). Una vez que se ha ingresado el código, aparecerán todos los registros asociados a él, incluyendo datos sobre impuestos, multas, deudas y juicios.
Si el RUT no está disponible, o si se quiere buscar información sobre una persona o empresa distinta a la propia, se pueden utilizar otros medios de búsqueda.
En primer lugar, se pueden consultar los listados de personas sancionadas por el SII. Estos listados están disponibles en la página web del SII (www.sii.cl), en la sección de “Sancionados”. Allí se pueden buscar personas por nombre y apellido, RUT, NIF o CIF.
También se pueden consultar las listas de empresas sancionadas por el SII. Estas listas están disponibles en la página web del SII (www.sii.cl), en la sección de “Empresas”. Allí se pueden buscar empresas por nombre, RUT o CIF.
Finalmente, se pueden utilizar buscadores en internet como Google, Yahoo! o Bing. Basta con escribir el nombre de la persona o empresa en cuestión para encontrar información en internet.
En cualquier caso, es importante tener en cuenta que la información contenida en estos listados es pública y que puede ser utilizada para fines ilícitos. Por ello, es recomendable consultar un abogado antes de tomar cualquier decisión.”
