Summary Disposition Legal Definition10 min read

A summary disposition legal definition is a quick and easy way to resolve a legal dispute without going to trial. This type of legal dispute resolution is typically used for minor offenses or cases in which the facts are not in dispute.
In a summary disposition, the parties involved in the legal dispute present their evidence to a judge, who then makes a ruling based on that evidence. If the judge finds that the defendant is guilty, the defendant may be sentenced immediately. If the judge finds that the defendant is not guilty, the case is dismissed.
Summary disposition is a less formal way to resolve a legal dispute than a trial. It is also less expensive and time consuming. However, it is important to note that a summary disposition is not always available. In some cases, a trial is the only way to resolve a legal dispute.
Table of Contents
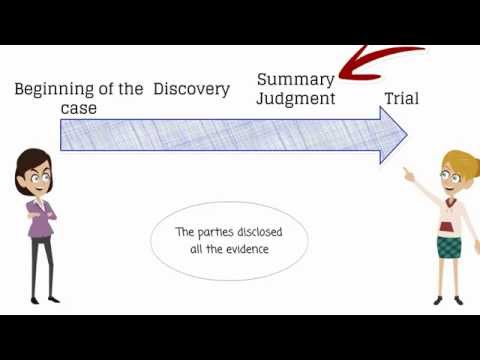
What does summary Judgement mean in legal terms?
A summary judgement is a type of judgement that is rendered by a court without a full trial. This type of judgement is typically used when the court believes that the facts of the case are clear and that there is no need for a full trial in order to reach a judgement. Summary judgement is also used to prevent parties from having to go to trial in order to resolve disputes.
When a party requests a summary judgement, the court will review the evidence that is presented and make a judgement based on that evidence. If the court determines that there is no genuine issue of material fact, then the court will grant the summary judgement to the party that requested it.
If there is a genuine issue of material fact, then the court will deny the summary judgement and the case will proceed to trial.
What is the purpose of a summary judgment?
A summary judgment, also known as a judgment on the pleadings, is a judgment that is rendered by a court without a full trial. This type of judgment is typically used when there is no dispute as to the facts of the case and the only issue is a legal one.
In order to obtain a summary judgment, the party who is seeking the judgment must file a motion with the court. This motion must include evidence that shows that there is no dispute as to the facts of the case and that the only issue is a legal one. If the court agrees that the motion is appropriate, it will issue a summary judgment in favor of the party who filed the motion.
There are a few reasons why a party might choose to seek a summary judgment. One reason is that a party might believe that they have a strong legal case and that a full trial is not necessary. Another reason is that a party might believe that a full trial would be too costly or time consuming.

The major advantage of a summary judgment is that it can help to speed up the litigation process. If the court agrees that a summary judgment is warranted, it will issue a judgment without requiring a full trial. This can save both time and money for the parties involved in the case.
However, there are also a few disadvantages to summary judgments. One disadvantage is that a party who loses a summary judgment motion may not have an opportunity to present their case in full at a trial. This can be a disadvantage if the party feels that they have a strong case and would like to present it to a jury.
Another disadvantage is that a party who loses a summary judgment motion may be liable for the other party’s costs and expenses. This can be a significant cost, particularly if the case is complex and the parties have spent a significant amount of time and money litigating the case.
In the end, whether or not to seek a summary judgment is a decision that must be made on a case-by-case basis. There are pros and cons to both sides, and the decision should be made based on the specific facts of the case.
Is a summary Judgement a good thing?
The short answer is a qualified yes. A summary judgement can be a very good thing for a litigant who is seeking to avoid the time and expense of a full-blown trial.
On the other hand, there are times when a party may be better off foregoing a summary judgement and instead proceeding to trial. There are several factors to consider when deciding whether to seek a summary judgement.
One of the primary benefits of a summary judgement is that it can save the parties time and money. A summary judgement can be granted when the parties agree on the facts of the case and the law governing the case.
This allows the parties to avoid the time and expense of a full-blown trial. In some cases, the parties may even be able to resolve the case without ever going to court.
Another benefit of a summary judgement is that it can help to resolve a case more quickly. This is especially helpful in cases where there is a risk of a party running out of time to bring a claim.
A summary judgement can also be helpful in cases where there is a risk that a party will not be able to present its case at trial. This is often the case in cases where the party is seeking to recover damages.
In some cases, a party may be better off proceeding to trial. There are several factors to consider when deciding whether to seek a summary judgement.
One of the primary factors to consider is the strength of the party’s case. If the party believes that it has a strong case, it may be better off proceeding to trial.
Another factor to consider is the amount of time and money that the party would save by proceeding to trial. If the party believes that it would save a significant amount of time and money by proceeding to trial, it may be worth considering.
Finally, the parties should consider the risk of not prevailing at trial. If the party believes that there is a significant risk of not prevailing at trial, it may be better off foregoing a summary judgement.
What is a summary of a legal case called?
A legal case is a formal proceeding in a court of law in which a plaintiff seeks a remedy against a defendant. In order to understand a legal case, one must first understand the legal system in which it takes place. There are two main types of legal systems in the world: civil law and common law.
Civil law is based on a written code of laws, while common law is based on judicial precedent. A legal case is a proceeding in a civil law court, while a lawsuit is a proceeding in a common law court.
A legal case begins when a plaintiff files a complaint with the court. The complaint sets out the facts of the case and the legal basis for the plaintiff’s claim. The defendant then has an opportunity to respond to the complaint.
After the defendant has responded, the court will schedule a hearing to determine the merits of the case. The hearing is a formal proceeding in which the parties will present their evidence and argue their case before a judge or jury.
If the court finds in the plaintiff’s favour, it will issue a judgement ordering the defendant to take certain actions or to pay the plaintiff a certain amount of money. If the defendant does not comply with the judgement, the plaintiff may seek to enforce it by filing a motion with the court.
A legal case may also be resolved through settlement. The parties may reach an agreement out of court, which will then be approved by the court.
So what is a summary of a legal case called? A legal case is a proceeding in a civil law court, while a lawsuit is a proceeding in a common law court. A legal case begins when a plaintiff files a complaint with the court, and it is resolved through settlement or a judgement issued by the court.
How do you respond to a summary Judgement?

When you receive a summary judgement, the first step is to determine whether you have grounds to oppose it. If you believe that the court made a mistake in its analysis or that you have evidence that wasn’t considered, you may be able to file an objection. You’ll need to act quickly, however, as there is usually a limited time frame in which to do so.
If you decide that there’s no chance of winning an objection, your next step is to decide whether to appeal. An appeal will allow you to argue your case before a higher court. It’s a more expensive and time-consuming process, however, and you’ll need to have a strong argument to be successful.
If you don’t believe that an appeal is worth your time and money, your final option is to negotiate a settlement with the other party. This can be a difficult process, but it may be the best option if you don’t think you’ll win an appeal or if you want to avoid the expense and hassle of going to court.
When should I apply for a summary Judgement?
When should I apply for a summary Judgement?
In civil court proceedings, a party may file a motion for a summary judgement if they believe that there is no genuine issue of material fact in dispute and that they are entitled to judgement as a matter of law. In order to be successful, the party filing the motion must demonstrate that they have a good faith basis for the belief that there is no genuine issue of material fact, and that they are likely to prevail on the merits.
There are a few factors to consider when deciding whether to file a motion for a summary judgement. First, you should assess whether there is a genuine issue of material fact in dispute. This can be done by reviewing the facts of the case and the evidence that is available. If there is no dispute as to the facts of the case, and the only issue is one of law, then a summary judgement may be appropriate.
You should also consider whether you are likely to prevail on the merits of the case. This can be done by reviewing the applicable law and the evidence that is available. If you can demonstrate that you are likely to win based on the evidence, then a summary judgement may be appropriate.
If you believe that you meet the requirements for a summary judgement, you should contact an attorney to discuss your case and determine whether a motion for a summary judgement is appropriate.
Who bears the burden in summary judgment?
Who bears the burden in summary judgment?
Summary judgment is a legal proceeding that allows a court to make a judgment on a case without a full trial. The party who is asking for summary judgment is called the movant, and the party who is opposing the motion is called the nonmovant. In order to win a motion for summary judgment, the movant must show that there is no genuine issue of material fact and that the movant is entitled to judgment as a matter of law.
The burden of proof in a motion for summary judgment is on the movant. The movant must show that there is no genuine issue of material fact and that the movant is entitled to judgment as a matter of law. This means that the movant must present evidence that supports its position and that there is no evidence to support the nonmovant’s position. If the movant can’t meet this burden, the motion for summary judgment will be denied.
