United States Judicial Circuits7 min read

The United States Judicial Circuits are the federal courts of appeal that are authorized by the Constitution and the laws of the United States. The Judicial Circuits are the first level of appeal for most cases that are filed in the federal court system. There are thirteen Judicial Circuits in the United States, and each Circuit has a court of appeals.
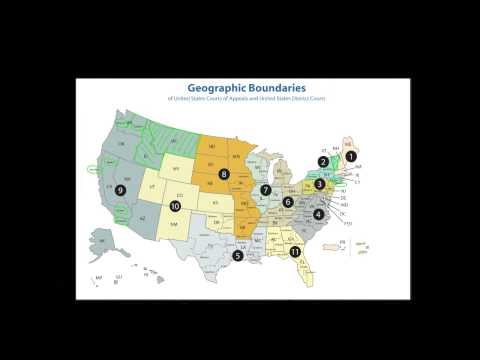
The Judicial Circuits are divided into two groups: the First Circuit, the Second Circuit, the Third Circuit, and the Fourth Circuit, and the Fifth Circuit, the Sixth Circuit, the Seventh Circuit, the Eighth Circuit, the Ninth Circuit, the Tenth Circuit, the Eleventh Circuit, and the D.C. Circuit. The First Circuit is located in Boston, the Second Circuit is located in New York City, the Third Circuit is located in Philadelphia, the Fourth Circuit is located in Richmond, the Fifth Circuit is located in New Orleans, the Sixth Circuit is located in Cincinnati, the Seventh Circuit is located in Chicago, the Eighth Circuit is located in St. Louis, the Ninth Circuit is located in San Francisco, the Tenth Circuit is located in Denver, the Eleventh Circuit is located in Atlanta, and the D.C. Circuit is located in Washington, D.C.
The Judicial Circuits have a variety of different responsibilities. The Circuit Courts of Appeals are responsible for reviewing the decisions of the district courts within their circuit. They are also responsible for issuing opinions in significant cases, and for sitting as a court of last resort in cases that have been appealed from the state courts. The Circuit Courts of Appeals are also responsible for appointing federal bankruptcy judges, and for hearing appeals from decisions of the Board of Immigration Appeals.
Table of Contents
How many judicial circuits are there in the United States?
There are 94 judicial circuits in the United States. These circuits are made up of federal district courts, which are the trial courts of the federal judiciary system. The circuit courts are the appellate courts for the district courts within their circuit. The Supreme Court is the only federal court that is not part of a judicial circuit.
What are the 12 federal circuits?
There are twelve federal circuits in the United States, and each one hears a different type of case. The Ninth Circuit is the largest, with 29 states in its jurisdiction, while the First Circuit is the smallest, with just six states.
The federal circuits were created in 1891 by Congress as a way to split up the caseload of the Supreme Court. Originally, there were just seven circuits, but Congress has added three more over the years.
Each circuit is made up of a number of districts, and each district has a federal court that hears cases. The court in the district that is closest to the defendant is known as the “venue court.”
The twelve federal circuits are:
The First Circuit: Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Puerto Rico, and Rhode Island
The Second Circuit: Connecticut, New York, and Vermont
The Third Circuit: Delaware, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania

The Fourth Circuit: Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia
The Fifth Circuit: Alabama, Florida, and Texas
The Sixth Circuit: Kentucky, Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee
The Seventh Circuit: Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin
The Eighth Circuit: Arkansas, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, and North Dakota
The Ninth Circuit: Alaska, Arizona, California, Guam, Hawaii, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, and Washington
The Tenth Circuit: Colorado, Kansas, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Utah, and Wyoming
The Eleventh Circuit: Alabama, Florida, and Georgia
The Twelfth Circuit: Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi
What are the federal judicial circuits?
There are thirteen federal judicial circuits in the United States, each one covering a specific region of the country. The jurisdiction of a federal judicial circuit includes federal district courts and appellate courts.
The first federal judicial circuit was created in 1801 by President John Adams. It consisted of the District of New Hampshire and the District of Maine. The number of circuits has changed over the years as states have been added or divided.
The current structure of federal judicial circuits was established in 1892 by Congress. There are currently thirteen circuits, each covering a specific region of the country. The circuit courts have original jurisdiction over cases arising under the Constitution, federal laws, and treaties. They also have appellate jurisdiction over cases from the district courts within their circuit.
The makeup of each federal judicial circuit can vary depending on the population and size of the states within the circuit. For example, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals covers nine western states, while the Second Circuit Court of Appeals covers only two states.
The primary function of the circuit courts is to interpret the law. They also hear appeals from the decisions of the district courts. In addition, the circuit courts have the authority to issue writs of mandamus, which are court orders requiring a government official to perform a specific act.
The federal judicial circuits are an important part of the judicial system in the United States. They ensure that the law is interpreted and applied evenly across the country.
What are the 3 court systems in the United States?
There are three court systems in the United States: the federal system, the state system, and the tribal system.
The federal system is the national court system. The federal courts have jurisdiction over cases involving the United States Constitution, federal laws, and federal treaties. The federal courts also have jurisdiction over cases involving certain types of civil and criminal cases, such as bankruptcy, copyright infringement, and terrorism.
The state court system is the court system for the individual states. The state courts have jurisdiction over cases involving state laws and state constitutional provisions.
The tribal court system is the court system for Native American tribes. The tribal courts have jurisdiction over cases involving tribal laws and tribal treaties.
Which states are in the 5th circuit?
The Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals is a federal appeals court with jurisdiction over Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas.
The Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals was created in 1845, when the Supreme Court split the Eighth Circuit into two circuits. The Fifth Circuit originally covered Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Louisiana. In 1879, the Fifth Circuit added Mississippi and Texas to its jurisdiction.
The Fifth Circuit is divided into two divisions: the Eastern Division, which covers Louisiana and Mississippi, and the Western Division, which covers Texas.
The Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals is based in New Orleans, Louisiana.
How many circuits are there?
How many circuits are there?

There are a lot of different ways to answer this question, because it can mean a lot of different things. But one way to answer it is to say that there are as many circuits as there are possible combinations of connections between two points.
This might not make a lot of sense to you, so let’s take a closer look at what it means.
When we talk about circuits, we’re usually talking about electrical circuits. These are circuits that allow electricity to flow through them.
electr·i·cal cir·cuit
noun
a path or network of connected wires, circuits, or devices through which an electric current flows.
So when we say there are as many circuits as there are possible combinations of connections between two points, what we’re really saying is that there are as many possible ways for electricity to flow through a circuit as there are possible ways for it to flow between two points.
And that’s a lot of possible ways!
If you took all the possible combinations of connections between two points and laid them out in a line, they would stretch for miles and miles.
So there are definitely a lot of circuits out there!
Who makes up the judicial branch?
The Judicial Branch of the United States government is made up of the nation’s federal courts and their system of law. It is made up of the Supreme Court, the country’s highest court, as well as a number of lower courts. The Judicial Branch is responsible for interpreting the law and resolving legal disputes.
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country and has the final say on all legal matters. It is made up of nine justices, who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The justices serve for life and must retire when they reach the age of 70. The Supreme Court hears a small number of cases each year, but its decisions are highly influential.
Lower courts are also part of the Judicial Branch. These courts hear a much greater number of cases and make decisions that are binding on lower courts. There are several different types of lower courts, including federal district courts, courts of appeals, and bankruptcy courts.
The Judicial Branch is responsible for interpreting the law and resolving legal disputes. It is an important part of the government and plays a critical role in our system of justice.
