What Does The Legal Term Tort Mean8 min read
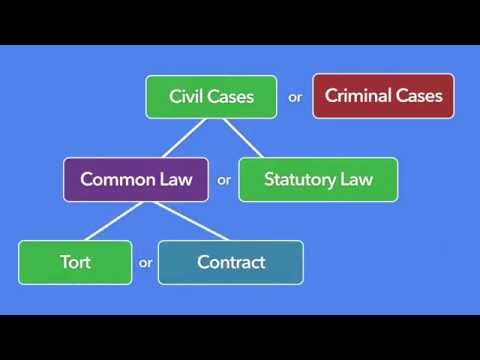
What is a tort?
A tort is a civil wrong that results in a legal liability. The person who commits the tort is called the tortfeasor. Torts can be intentional or unintentional.
Intentional torts are those that are committed on purpose, such as assault and battery. Unintentional torts are those that are not committed on purpose, such as negligence.
Torts can be broken down into several categories:
• Intentional torts
• Negligence
• Product liability
• Defamation
• Breach of contract
What is the difference between a tort and a crime?
The main difference between a tort and a crime is that a tort is a civil wrong, while a crime is a criminal wrong. A tort can result in a civil lawsuit, while a crime can result in criminal prosecution.
Table of Contents
What is an example of a tort?
A tort is a wrongful act or omission that results in injury to another. Torts can be intentional or unintentional. Some of the most common torts include negligence, trespassing, and libel or slander.

Negligence is the most common tort. It occurs when a person fails to exercise the degree of care that a reasonable person would exercise in a similar situation. For example, if a driver does not stop at a stop sign and hits another car, that would be considered negligence.
Trespassing is entering onto someone else’s property without permission. Trespassing can be a civil or criminal offense, depending on the circumstances.
Libel and slander are two types of defamation. Libel is written defamation, while slander is spoken defamation. To be considered defamation, the statement must be false and must cause injury to the person’s reputation.
What are the three elements of a tort?
The three elements of a tort are duty, breach, and damages.
A tort is a wrongful act that results in injury to someone else. The three elements of a tort are duty, breach, and damages.
Duty is the legal obligation to behave in a certain way. Breach is the failure to meet that obligation. Damages are the harm that is suffered as a result of the breach.
Tort law is a branch of civil law that deals with wrongful acts. Torts can be intentional or accidental. Intentional torts are intentional acts that cause harm to another person. Accidental torts are accidents that cause harm to another person.
Tort law is used to protect the rights of injured parties. Victims of tortious conduct can sue the person or company that caused their injuries. Tort law allows injured parties to recover damages for their losses.
The three elements of a tort are duty, breach, and damages. Duty is the legal obligation to behave in a certain way. Breach is the failure to meet that obligation. Damages are the harm that is suffered as a result of the breach. Tort law is a branch of civil law that deals with wrongful acts. Torts can be intentional or accidental. Intentional torts are intentional acts that cause harm to another person. Accidental torts are accidents that cause harm to another person. Tort law is used to protect the rights of injured parties. Victims of tortious conduct can sue the person or company that caused their injuries. Tort law allows injured parties to recover damages for their losses.
What does it mean to sue in tort?
What does it mean to sue in tort?
Tort law is a branch of civil law that allows an injured person to file a lawsuit against the person or entity that caused their injury. Torts can be intentional or unintentional, and can result in both economic and non-economic damages.
There are several reasons why someone might choose to sue in tort. Perhaps the most common reason is to recover damages for injuries that have been sustained. This might include physical injuries, as well as emotional or psychological injuries. Tort law can also be used to enforce contracts, or to seek redress for wrongs that have not been addressed in a contract.

Tort law is also used to protect private individuals from certain types of harm. For example, a person might file a tort lawsuit if they were injured by a defective product. Tort law can also be used to protect people from slander or libel.
In order to file a tort lawsuit, the injured person must typically prove that the person or entity that caused their injury was negligent. This can be a difficult task, and often requires the help of an experienced tort lawyer.
If you have been injured and believe that you may have a case, it is important to speak to an attorney as soon as possible. The sooner you get started, the sooner you can start recovering damages for your injuries.
What is the simplest tort?
A tort is a wrongful act or omission that results in injury to another person. Torts can be classified in a number of ways, but one common way is to group them according to their simplicity. The simplest torts are those that involve a direct injury to someone’s person or property.
The most common type of direct tort is personal injury. This occurs when someone is injured as a result of the negligence or intentional act of another person. For example, if someone is hit by a car that was being driven negligently, that would be a personal injury tort.
Another common type of direct tort is property damage. This occurs when someone damages or destroys someone else’s property. For example, if someone throws a rock through a window, that would be a property damage tort.
There are also a number of indirect torts, which involve injuries that are not caused by a direct act or omission. These torts can be more complicated to prove, and often require the help of an attorney. Some of the most common indirect torts include product liability, negligence, and defamation.
If you have been injured as a result of another person’s wrongful act or omission, you may be able to sue for damages. It is important to speak with an attorney to determine whether you have a valid tort claim.
What are the 4 most common torts?
There are many different types of torts, but four of the most common are negligence, intentional infliction of emotional distress, defamation, and invasion of privacy.
Negligence is the most common tort. It occurs when a person breaches a duty of care that they owe to another person, and that breach results in harm. For example, if a driver fails to yield to oncoming traffic and causes a car accident, they may be liable for the damages caused.
Intentional infliction of emotional distress is a tort that arises when a person intentionally causes severe emotional distress to another person. This can include things like yelling at someone, spreading rumors about them, or even stalking them.

Defamation is the tort of injuring someone’s reputation by spreading false information about them. This can include making false statements about someone in public, writing defamatory statements in a document, or even posting them online.
Invasion of privacy is the tort of unlawfully intruding into someone’s personal life. This can include things like spying on someone, recording them without their consent, or even publishing private information about them.
What are the 3 types of torts?
There are three main types of torts: intentional, negligent, and strict liability.
Intentional torts are cases where the defendant deliberately caused harm to the plaintiff. This might include assault, battery, or defamation.
Negligent torts are cases where the defendant failed to act reasonably and caused harm to the plaintiff. This might include car accidents or medical malpractice.
Strict liability torts are cases where the defendant is held responsible even if they did not cause the harm. This might include product liability or environmental pollution.
Who Cannot sue for tort?
When most people think of a lawsuit, they think of someone suing another person for money. But a lawsuit can be brought for many reasons, including injury or damage to property. In some cases, people may be wondering who cannot sue for tort.
The general rule is that anyone can sue for tort. This includes individuals, businesses, and even government entities. However, there are some exceptions to this rule.
One example of an exception is the doctrine of sovereign immunity. This doctrine holds that the government cannot be sued without its consent. So, for example, if you are injured by a government employee, you may not be able to sue the government itself.
Another exception is the principle of charitable immunity. This principle holds that charities cannot be sued for negligence. So, for example, if you are injured by a charity’s employee, you may not be able to sue the charity.
There are also some situations where individuals cannot sue for tort. For example, if you are injured as a result of a crime, you may not be able to sue the criminal. This is because the criminal is not liable for the injury.
There are also some situations where businesses cannot sue for tort. For example, if you are injured as a result of a defective product, you may not be able to sue the manufacturer. This is because the manufacturer is not liable for the injury.
So, who can sue for tort? Generally, anyone can sue for tort. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, including the doctrine of sovereign immunity and the principle of charitable immunity. Additionally, there are some situations where individuals cannot sue for tort, and some situations where businesses cannot sue for tort.
