What Is A Tort Legal Definition8 min read

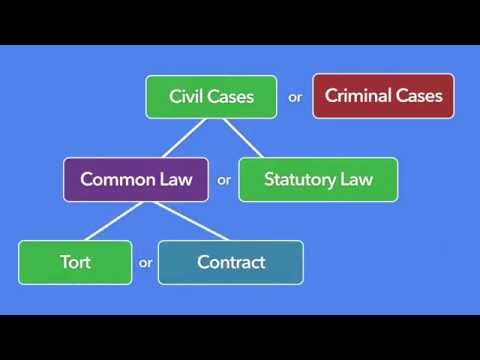
A tort is a legal term that refers to a wrongful act, or an injury, that is not a criminal act. Torts can be intentional, or they can be the result of careless or reckless behavior. A tort can be something that causes physical harm, such as an assault or a car accident. Torts can also be things that cause emotional harm, such as slander or invasion of privacy.
Tort law is the area of law that deals with torts. Tort law is divided into two main categories: negligence and intentional torts. Negligence torts are injuries that are caused by someone’s careless or reckless behavior. Intentional torts are injuries that are caused by someone’s intentional act.
In order to win a tort case, the plaintiff must show that the defendant caused them harm, that the harm was not intentional, and that the harm was not caused by the plaintiff’s own negligence. The plaintiff must also show that the harm resulted in some type of loss or damage.
Tort law is based on the principle of negligence. This principle states that people should take reasonable steps to avoid harming others. If they don’t take these reasonable steps, and they harm someone else, they can be held liable for the harm that they caused.
Tort law is different from criminal law. Criminal law is the area of law that deals with crimes. Crimes are defined as wrongful acts that are punishable by law. Torts are not punishable by law, and they are not considered crimes.
Tort law is based on the principle of negligence. This principle states that people should take reasonable steps to avoid harming others. If they don’t take these reasonable steps, and they harm someone else, they can be held liable for the harm that they caused.
Table of Contents
What is the legal definition of torts?
A tort is a wrongful act, other than a breach of contract, for which a civil action can be brought. A tort is usually defined as a civil wrong that results in injury to another party. Torts may be intentional, such as assault and battery, or unintentional, such as negligence.
There are three elements that must be present in order for a tort to exist:
1. an act or omission;
2. resulting in damage or injury; and
3. to a person or their property.

Torts can be divided into four main categories:
1. intentional torts – these are torts that are committed intentionally, such as assault, battery, and false imprisonment.
2. negligence torts – these are torts that are caused by negligence, such as car accidents and medical malpractice.
3. strict liability torts – these are torts for which the defendant is held strictly liable, even if they were not negligent, such as product liability cases.
4. torts against property – these are torts that involve damage to or loss of property, such as trespass and conversion.
What is an example of a tort?
A tort is a wrongful act that results in harm to another person or their property. Torts can be intentional or unintentional, and can include both civil and criminal offenses. Some of the most common torts include assault, battery, defamation, and negligence.
Assault is the act of threatening or attempting to harm another person. Battery is the act of actually harming another person. Defamation is the act of making false statements about another person that damage their reputation. Negligence is the failure to exercise the degree of care that a reasonable person would in a similar situation.
Torts can have a variety of consequences, including monetary damages, injunctions, and damages to one’s reputation. Anyone who has been harmed as a result of another person’s wrongful act can file a tort claim. It is important to note that there is a statute of limitations in place for tort claims, so it is important to file a claim as soon as possible.
What are the 3 types of torts?
There are three types of torts: intentional, negligent, and strict liability.
Intentional torts are actions that are done on purpose and with malice. An intentional tort can be anything from assault and battery to defamation.
Negligent torts are accidents that could have been prevented if the person had been more careful. For example, if someone is driving and they hit a pedestrian because they were not paying attention, that would be a negligent tort.
Strict liability torts are accidents that are not the fault of anyone in particular, but the person or company who is responsible is still held liable. For example, if a company manufactures a product that is later found to be defective and causes someone harm, the company would be liable under a strict liability tort.
What is the simplest tort?
The simplest tort is a civil wrong that results in damages to another person. Torts are usually broken down into three categories: intentional torts, negligence torts, and strict liability torts.
Intentional torts are acts that are done on purpose, such as assault, battery, and trespass. Negligence torts are acts that are done negligently, such as car accidents or medical malpractice. Strict liability torts are acts that do not require any negligence on the part of the defendant, such as product liability or animal attacks.
The easiest way to understand torts is to think of them as accidents that could have been prevented. For example, if you are in a car accident, that is a negligence tort. If you are attacked by a dog, that is a strict liability tort. If someone punches you, that is an intentional tort.
Torts can be complicated, but the basic idea is simple. If you are injured or have your property damaged because of someone else’s actions, you may be able to sue for damages.
What is an example of a tort case?
What is an example of a tort case?
One example of a tort case is when someone is injured as a result of another person’s negligence. For example, if a driver runs a red light and causes a car accident, the injured parties may sue the driver for damages. Torts can also include property damage, libel, and other wrongful acts.
Tort cases can be quite complex, and it is important to have an experienced attorney represent you if you are involved in one. The laws governing tort cases vary from state to state, so it is important to consult with an attorney who is familiar with the specific laws in your area.
If you have been injured or have suffered damages as a result of another person’s actions, you may wish to speak with an attorney about filing a tort case.

What is another word for tort?
A tort is a civil wrong that results in injury to another person or their property. Torts can be intentional or unintentional. Some of the most common torts include negligence, defamation, and trespass.
Torts are often categorized as intentional torts or negligent torts. Intentional torts are those that are committed on purpose, while negligent torts are those that are caused by carelessness or lack of attention.
Some of the most common intentional torts include assault, battery, and false imprisonment. Assault is the act of threatening someone with violence, while battery is the actual act of violence. False imprisonment is the unlawful detention of someone.
Negligent torts can include car accidents, slip and fall accidents, and medical malpractice. Car accidents happen when one driver is careless and causes a collision, slip and fall accidents happen when someone is injured because of a dangerous condition on someone else’s property, and medical malpractice happens when a doctor makes a mistake that causes injury to a patient.
Torts can also be classified as economic torts or personal injury torts. Economic torts are those that involve damage to property or financial loss, while personal injury torts are those that involve physical or emotional injury.
If you have been injured because of someone else’s negligence, you may be able to sue them for damages. Damages can include medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering. To learn more about torts and how to sue for damages, contact an attorney.
What are the 4 most common torts?
There are four main types of torts: negligence, intentional torts, defamation, and product liability.
Negligence is the most common type of tort. It occurs when someone breaches a duty of care that they owe to another person, and that breach causes harm. For example, if a driver does not stop at a stop sign and hits another car, they would be liable for the damages caused by the accident.
Intentional torts occur when someone deliberately harms another person. For example, assault and battery are intentional torts.
Defamation is the publication of a false statement that damages someone’s reputation. For example, if someone publishes a false article about a person that accuses them of a crime they did not commit, they would be liable for defamation.
Product liability is the legal responsibility of a manufacturer to compensate someone who is injured by a defective product. For example, if a product explodes and injures someone, the manufacturer would be liable for the damages.
