Company As A Legal Entity10 min read
A company is a business entity that is authorized to operate in a specific jurisdiction. The company is a legal entity, separate from its owners. This separation protects the company’s owners from personal liability for the company’s debts and obligations.
A company can be formed in a number of ways, depending on the jurisdiction. The most common way to form a company is to file articles of incorporation with the government. The articles of incorporation will set out the company’s name, purpose, and shareholders.
The company’s shareholders are responsible for electing the company’s directors. The directors are responsible for managing the company’s affairs. The company must file annual reports with the government, and the directors must file financial statements with the shareholders.
The company is a separate legal entity from its shareholders and directors. The company can enter into contracts, own property, and sue and be sued. The company’s shareholders and directors are not personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. This separation protects the company’s owners from personal liability.
A company can be a powerful tool for businesses. The company can own property, enter into contracts, and sue and be sued. The company’s shareholders and directors are not personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. This separation protects the company’s owners from personal liability.
Table of Contents
What makes a company a legal entity?
A legal entity is a company, organization, or group that has been granted a legal status by a government. This means that the entity has certain rights and responsibilities under the law. There are many types of legal entities, but the most common are corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs).
A company becomes a legal entity by registering with the government. The company must file articles of organization or a similar document and pay a registration fee. Once the company is registered, it is legally separate from its owners and can enter into contracts and sue or be sued.
A legal entity has a number of advantages over a sole proprietorship or partnership. First, it is a separate legal entity and can sue or be sued. Second, it can enter into contracts and is not personally liable for the debts of the company. This means that the owners of the company are not responsible for the company’s debts if it goes bankrupt. Finally, a legal entity can raise money by issuing stock or bonds.
There are a number of disadvantages to forming a legal entity. First, it is more expensive to set up and maintain than a sole proprietorship or partnership. Second, a legal entity is subject to more regulations than a sole proprietorship or partnership. Finally, a legal entity can be harder to manage than a sole proprietorship or partnership.
Is company a legal entity type?

Is a company a legal entity type? This is a question that many people may ask, and the answer is not always straightforward. In general, a company is a legal entity, meaning that it has a separate legal identity from its owners. This means that the company can enter into contracts, own property, and sue and be sued in its own name.
There are different types of companies, each with their own rules and regulations. The most common type of company is a corporation. A corporation is a company that is registered with the government and has separate legal status from its owners. A corporation can have shareholders, who own shares in the company and have a say in how it is run.
Another type of company is a limited liability company (LLC). An LLC is a company that is registered with the government, but does not have separate legal status from its owners. This means that the company is not a separate legal entity, and the owners are personally liable for the company’s debts and obligations.
There are also partnerships and sole proprietorships, which are not companies per se, but rather business structures. A partnership is a business that is owned by two or more people, and a sole proprietorship is a business that is owned by one person. These business structures are not registered with the government and do not have separate legal status from their owners.
So, to answer the question, a company is a legal entity type, but there are different types of companies, each with their own rules and regulations.
What is an example of a legal entity?
A legal entity is a term used in business law to describe a group of people or organizations that are recognized by law as being able to act as a single entity. This means that the entity can enter into contracts, own property, and sue and be sued in its own name.
One of the most common types of legal entities is a corporation. This is a type of business organization that is created by filing Articles of Incorporation with the state. A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners and has its own legal rights and responsibilities.
Another common type of legal entity is a limited liability company (LLC). An LLC is a type of business organization that provides limited liability protection to its owners. This means that the owners of an LLC are not personally liable for the debts and obligations of the company.
There are many other types of legal entities, including partnerships, sole proprietorships, and nonprofit organizations. Each of these entities has its own unique set of rules and regulations that must be followed. It is important to consult with an attorney if you are considering forming a legal entity for your business.
What are the 5 main types of legal entity a business can be?
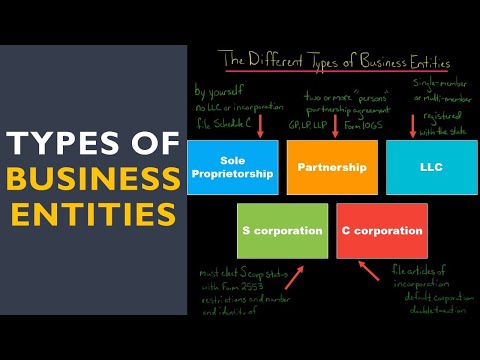
There are five main types of legal entity a business can be: a sole proprietorship, a partnership, a limited liability company (LLC), a corporation, and a S corporation.

1. A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common type of business structure. It is owned and operated by a single individual and has no separate legal existence from the owner. All profits and losses are taxed on the owner’s personal income tax return.
2. A partnership is a business owned by two or more individuals. Partners share in the profits and losses of the business and are personally liable for its debts. Partnerships are not taxed as separate entities, but profits and losses are passed through to the individual partners and taxed on their personal income tax returns.
3. An LLC is a business structure that combines the limited liability of a corporation with the tax flexibility of a partnership. LLCs are not taxed as separate entities, but profits and losses are passed through to the individual members and taxed on their personal income tax returns.
4. A corporation is a legal entity that is separate and distinct from its owners. It is taxed as a separate entity, and its owners are not personally liable for its debts.
5. A S corporation is a special type of corporation that is taxed like a partnership. S corporations are limited to 100 shareholders and are not subject to the double taxation that occurs with regular corporations.
What legal entity means?
When starting a business, one of the first decisions to make is what legal entity to form. This decision will determine how your business is structured and what liabilities and protections it has.
There are four types of legal entities: sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, and limited liability company (LLC).
The most common type of legal entity is the corporation. A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners and has its own legal rights and liabilities. The owners of a corporation are called shareholders and have limited liability for the corporation’s debts and obligations. This means that if the corporation goes bankrupt, the shareholders cannot be held liable for its debts.
A limited liability company is a newer type of legal entity that combines the benefits of a corporation and a partnership. LLCs offer limited liability for their owners and are less expensive and easier to set up than corporations.
The final type of legal entity is the sole proprietorship. A sole proprietorship is not a separate legal entity and has no legal rights or liabilities. The owner of a sole proprietorship is personally liable for its debts and obligations.

When deciding which legal entity to form, it is important to consider the risks and benefits of each type. Each type of legal entity has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks, so it is important to choose the one that best suits your business.
What is the difference between legal entity and company?
There is a big difference between legal entities and companies. A legal entity is a term used to describe any entity that has specified legal rights and obligations, while a company is a type of legal entity.
One of the key differences between a legal entity and a company is that a company is a separate legal entity from its shareholders. This means that the shareholders are not personally liable for the debts and obligations of the company. A legal entity, on the other hand, is liable for its own debts and obligations, regardless of who owns or controls it.
Another key difference is that a company can own and control other legal entities, while a legal entity cannot own or control a company.
A company must also comply with certain corporate governance requirements, such as having an independent board of directors and maintaining accurate financial records. A legal entity is not required to comply with these requirements.
Finally, a company is a more complex and expensive legal structure to set up and maintain than a legal entity.
What do you mean by legal entity?
A legal entity is a term used in business law to denote a company or other organization that is recognized as a separate entity from its owners. A legal entity has its own rights and liabilities, and can enter into contracts and own assets. It is distinct from its owners in that it can continue to exist even if they sell all or part of their shares.
There are a number of different types of legal entities, including corporations, limited liability companies, and partnerships. Each type has its own specific rules and regulations, and it is important to understand the differences between them before setting up a business.
A corporation is a type of legal entity that is separate and distinct from its owners. It is typically a for-profit company, and its shareholders are liable for the company’s debts only to the extent of their investment in the company. A corporation is governed by a board of directors, and must file articles of incorporation with the state in order to form.
A limited liability company (LLC) is a type of business that offers the limited liability of a corporation, while retaining the pass-through taxation of a partnership. An LLC is a hybrid entity, and can be taxed as either a corporation or a partnership, depending on the preferences of its owners. LLCs are typically used for small businesses, and must file articles of organization with the state in order to form.
A partnership is a type of business organization that is owned by two or more people. Partners are personally liable for the debts of the business, and the partnership itself does not have any separate legal status. Partnerships must file a partnership agreement with the state in order to form.
