Legal Definition Of Tort7 min read

What is tort?
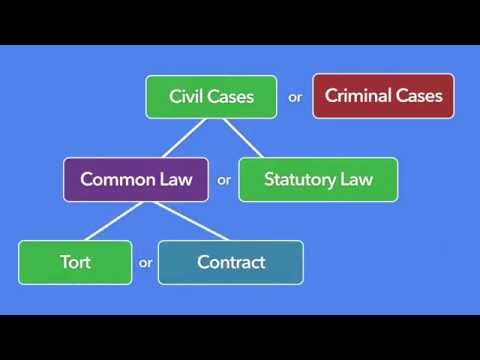
Tort is a legal term that refers to a civil wrong. A tort can be committed by an individual or an organization and can result in a civil lawsuit.
What are the different types of tort?
There are several different types of tort, including negligence, intentional infliction of emotional distress, libel, and slander.
What is negligence?
Negligence is the most common type of tort. It occurs when a person or organization fails to exercise a reasonable level of care, and as a result, someone is injured or suffers damages.
What is intentional infliction of emotional distress?
Intentional infliction of emotional distress is a tort that occurs when someone intentionally causes severe emotional distress to another person. This type of tort can be difficult to prove, and often requires the testimony of a qualified expert.
What is libel?
Libel is a tort that occurs when someone publishes false or damaging information about another person. This information must be published in a printed or electronic media.
What is slander?
Slander is a tort that occurs when someone verbally publishes false or damaging information about another person. Unlike libel, slander does not require that the information be published in a printed or electronic media.
Table of Contents
What are the 3 types of torts?

There are three types of torts: intentional, negligent, and strict liability.
Intentional torts are those in which the plaintiff can prove that the defendant intentionally harmed them. For example, assault and battery are intentional torts.
Negligent torts are those in which the plaintiff can prove that the defendant was negligent in their actions, and that this negligence caused harm to the plaintiff. For example, a car accident that was caused by the defendant’s negligence would be a negligent tort.
Strict liability torts are those in which the plaintiff can prove that the defendant is liable, even if they were not negligent. For example, product liability cases are strict liability torts.
What is an example of a tort?
A tort is a wrongful act that results in injury to another party. Torts can be both civil and criminal, and can range in severity from a minor altercation to a serious accident. Some of the most common torts include negligence, defamation, and product liability.
Negligence is the most common tort, and is defined as the failure to exercise the standard of care that a reasonable person would in a similar situation. This can include things like driving recklessly, neglecting to maintain a property, or not taking safety precautions when working with hazardous materials.
Defamation is the publication of false information that injures a person’s reputation. This can include libel (writing or publishing false statements) or slander (spoken false statements).
Product liability is a type of tort that holds manufacturers and sellers liable for injuries caused by defective products. This can include products that are dangerous, contain harmful ingredients, or are not properly labeled.
What are the 4 necessary elements of a tort?
A tort is a civil wrong that results in harm to another person or their property. To be successful in a tort case, the injured party must prove that the defendant owed them a duty of care, that they breached that duty, that the breach caused the injury, and that the injury resulted in damages.
The four necessary elements of a tort are duty of care, breach of duty, causation, and damages.
Duty of Care
The first element is duty of care. The injured party must prove that the defendant owed them a duty of care. This can be established in a number of ways, such as by statute or by common law.
Breach of Duty
The second element is breach of duty. The injured party must prove that the defendant breached their duty of care. This can be established by showing that the defendant failed to meet the standard of care that a reasonable person would have met in the same situation.
Causation
The third element is causation. The injured party must prove that the defendant’s breach of duty caused the injury. This can be established by showing that the injury would not have occurred but for the defendant’s breach of duty.
Damages
The fourth and final element is damages. The injured party must prove that they suffered damages as a result of the defendant’s breach of duty. This can be established by showing that the injury resulted in financial losses, physical injuries, or emotional distress.
What are the 5 elements of a tort?
A tort is a wrongful act that results in injury to another party. There are five elements that must be present in order for a tort to be established.
1. The act must be intentional or negligent. The act must be something that the defendant did on purpose, or something that they should have known would result in harm. If the act was accidental, it is not a tort.
2. The act must cause harm to another party. The harm can be physical, financial, or emotional.
3. The harm must be a direct result of the act. If the harm could have happened even if the act hadn’t occurred, it is not a tort.
4. There must be a damages award. The party that was harmed must be able to show that they suffered some type of loss that can be compensated.
5. The party that was harmed must file a lawsuit. The party must go to court and sue the person or company that caused the harm.

Who Cannot be sued in tort?
There are a number of people and organizations who cannot be sued in tort. This includes the government, the Crown, the police, and members of the armed forces. These organizations are immune from civil action, meaning that they cannot be sued for damages.
One of the reasons for this immunity is to protect the public from the risk of legal action paralyzing important public functions. For example, the government cannot be sued every time someone slips and falls on a wet sidewalk. This would create an undue financial burden and prevent the government from carrying out its duties.
The immunity of the government and other organizations also serves to protect individual members of those organizations from frivolous lawsuits. If everyone who works for the government or the police could be sued every time they made a mistake, they would be at risk of financial ruin. This would make it difficult for them to do their jobs effectively.
There are some limited exceptions to the immunity of the government and other organizations. For example, if a government employee commits a crime, they can be sued in tort. However, the government itself cannot be sued for the employee’s actions.
The immunity of the government and other organizations is also subject to change. For example, the UK government recently waived its immunity in cases of sexual abuse by members of the military. This change was made in response to the overwhelming public pressure to hold the government accountable for the actions of its employees.
So, who cannot be sued in tort? The government, the Crown, the police, and members of the armed forces are immune from civil action. There are some limited exceptions, and the immunity of these organizations is subject to change.
What is another word for tort?
Tort is a term used in the law to describe a civil wrong. A tort can be either intentional or accidental. Torts can give rise to a civil action for damages. The most common type of tort is negligence, which occurs when a person breaches a duty of care which causes harm to another person. Other common torts include defamation, trespass, and product liability.
What are the 4 most common torts?
Torts are a specific type of civil law that deals with the wrongful act or omission of one person that injures another person. There are many different types of torts, but the four most common are negligence, intentional infliction of emotional distress, defamation, and invasion of privacy.
Negligence is the most common tort and is defined as the failure to exercise the standard of care that a reasonably prudent person would in a similar situation. This can include things such as driving negligently or failing to properly maintain property.
Intentional infliction of emotional distress is the intentional and extreme infliction of emotional distress on another person. This can include things such as verbal abuse, harassment, or threats.
Defamation is the publication of a false statement that injures the reputation of another person. This can include libel (written defamation) and slander (verbal defamation).
Invasion of privacy is the unauthorized intrusion into someone’s private affairs that causes them distress. This can include things such as spying on someone, publishing private information, or using someone’s image without their consent.
